Poland’s IT sector attracts major global firms like Google and Microsoft, but the operating environment is changing. As the European Union enforces stricter governance, EU regulations IT Poland are reshaping recruitment strategies.
The focus has moved beyond simple talent acquisition to rigorous compliance, specifically regarding GDPR Poland standards for data privacy and the AI Act Poland implications for automated screening.
For international firms, navigating these legal frameworks is no longer optional, it is the prerequisite for hiring the region’s skilled workforce without risking significant fines.
The Polish Tech Landscape: A Magnet for Global Talent
Poland’s position as a top EU outsourcing destination is bolstered by a massive talent pool and a mature business ecosystem. The sector employs over 450,000 professionals in modern business services, with the broader ICT market boasting over 650,000 IT professionals.
With unemployment in the sector remaining negligible (often under 5%) and major hubs like Warsaw, Kraków, and Wrocław maturing into full-fledged innovation centers, the competition for talent is fierce.
| Metric | Value | Notes |
| IT professionals | 650,000 | Across ICT sector |
| Modern Business Services workforce | 450,000 | Includes AI, software, cloud roles |
| Unemployment in IT | <5% | Very competitive market |
| Annual STEM graduates | 110,000 | Increasingly English-proficient |
| Top hubs | Warsaw, Kraków, Wrocław | Main innovation centers |
Hiring Challenges and Talent Supply
Despite the booming market, companies face acute shortages in specialized roles such as AI, software engineering, and data science. The demand for AI/ML roles alone has seen a surge of nearly 70%, driven by global digitalization trends.
Poland feeds this demand with a robust educational pipeline, producing over 110,000 annual STEM graduates who are increasingly proficient in English and modern tech stacks.
- Talent Gap: High demand for seniors in Python, Java, and Cloud architectures.
- Graduate Pipeline: Strong flow of junior talent from top technical universities.
- Retention: Candidates prioritize stability and clear career paths.
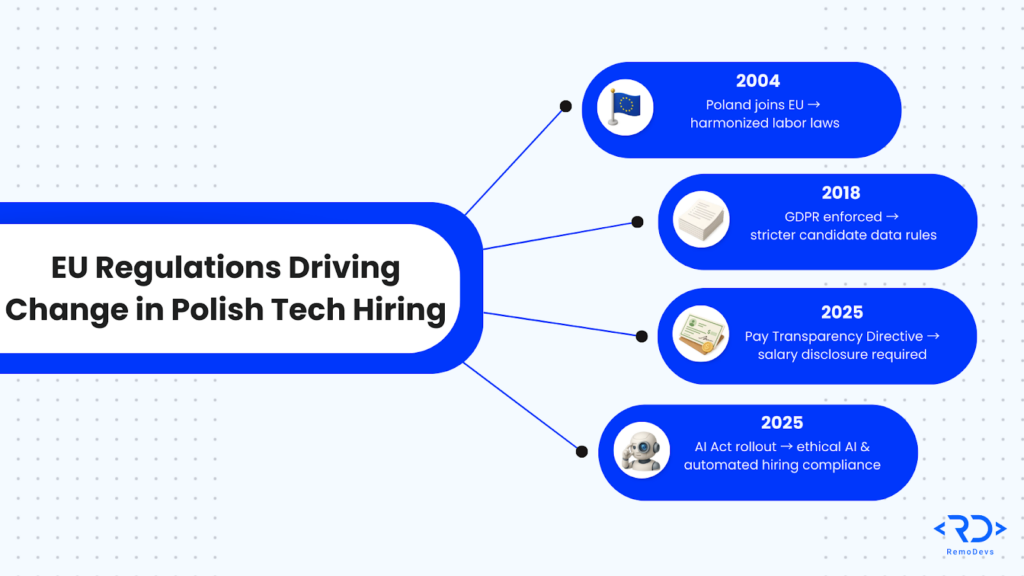
Since joining the EU in 2004, Poland has harmonized its labor laws with European standards, creating a predictable environment for foreign investors. As of 2025, the integration of new directives, such as the Pay Transparency Directive, is further standardizing the market.
This alignment ensures that EU regulations IT Poland serve as a quality seal, boosting cross-border recruitment by guaranteeing that Polish teams operate under the same high standards as their Western counterparts.
GDPR in Poland: Safeguarding Candidate Data in Tech Recruitment
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) fundamentally altered how candidate data is handled, and GDPR Poland (enforced by the Personal Data Protection Office, or UODO) is particularly strict in employment contexts.
The Polish Labor Code aligns with GDPR to strictly limit data minimization, meaning recruiters can only request data necessary for the specific role.
Impact on Hiring Processes
The days of harvesting candidate data without clear purpose are over. Tech companies must now navigate strict limitations on background checks and monitoring. For example, requesting a “certificate of no criminal record” is only permissible for specific roles (e.g., finance or security), not for a standard frontend developer.
- CV Data: Storing CVs for “future recruitment” requires separate, explicit consent.
- Background Checks: Strictly limited; social media scraping for profiling can be a violation.
- DPIAs: Data Protection Impact Assessments are often mandatory for large-scale processing of candidate data.
To avoid fines – which can reach up to 4% of global turnover – companies must implement robust privacy notices in job postings and ensure secure data storage. For IT recruitment agencies in Poland, this means maintaining transparent data flows and guaranteeing that remote hiring processes do not inadvertently breach cross-border transfer rules.
Polish IT companies are increasingly adopting ISO 27001 standards to demonstrate this compliance to international partners.
GDPR Compliance Checklist for Tech Hiring in Poland
- Data Collection: Collect only what is legally required (e.g., education, experience).
- Consent Management: Obtain separate checkboxes for current vs. future recruitment.
- Breach Notification: Mandatory reporting of data leaks to UODO within 72 hours.
- Employee Rights: Clear right to be forgotten and access to stored data.
- Fines & Audits: Regular internal audits to prevent revenue-threatening penalties.
The AI Act in Poland: Ethical AI and the Future of Automated Hiring
The AI Act Poland represents the next frontier in regulatory compliance. Under the EU AI Act, recruitment tools that use AI to filter applications, evaluate candidates, or conduct interviews are classified as High-Risk AI Systems.
While the full regulation sees a phased rollout, Poland has been proactive, with the draft Act on AI Systems (February 2025 version) laying the groundwork for a national “AI Office” to oversee compliance and support innovation through regulatory sandboxes.
Direct Effects on Tech Recruitment
The implications for automated hiring are profound. “Black box” algorithms that reject candidates without explanation are now illegal. Recruitment tools must be transparent, explainable, and free from bias, a significant challenge given that many legacy ATS (Applicant Tracking Systems) were not built with these standards in mind.
- Bias Prevention: Algorithms must be tested to ensure they don’t discriminate against gender or ethnicity.
- Transparency: Candidates must be informed if they are interacting with an AI (e.g., chatbots).
- Human Oversight: A human recruiter must have the final say in high-stakes hiring decisions.
Poland is adapting to this shift through initiatives like the AI Policy 2030, which focuses on upskilling the workforce. However, a gap remains; there is a shortage of experts capable of auditing these AI systems for compliance. For companies looking to hire data scientists or AI ethicists, this creates a new niche of high-demand roles.
High-Risk AI Applications in Tech Hiring Under AI Act
- Automated CV Screening: Parsing resumes to rank candidates based on keywords.
- Predictive Analytics for Fit: Using historical data to predict a candidate’s future success.
- Chatbots for Interviews: AI agents conducting preliminary screening interviews.
- Facial Recognition: Emotion analysis tools in video interviews (strictly regulated/banned).
Broader EU Directives: Transparency and Labor Rights in Polish IT
Beyond GDPR and AI, broader social directives are reshaping the employee value proposition. The Pay Transparency Directive, with key Polish implementation deadlines in December 2025, requires employers to disclose initial salary ranges or rates in job postings or prior to interviews.
This is a game-changer for IT recruitment trends in Poland, forcing companies to move away from “competitive salary” placeholders to clear, objective pay bands.
- Salary Disclosure: Mandatory salary ranges in job ads or before the first interview.
- Gender Pay Gap: Large firms will eventually need to report and remediate gaps exceeding 5%.
- Remote Work: Updated Labor Code rules clarify remote work compensation (e.g., electricity/internet stipends).
These shifts link back to the core theme of EU regulations IT Poland: a move toward a more transparent, candidate-centric market. This transparency helps attract senior talent who value openness and reduces time-wasted on mismatched salary expectations.
Challenges and Strategic Opportunities for Tech Firms
The regulatory wave brings hurdles. Compliance costs are rising, and the administrative burden of documenting data processing and AI usage is significant.
Furthermore, the industry faces a gender disparity challenge, women make up 28% of the workforce in AI-impacted jobs compared to 17% of men, highlighting the need for inclusive hiring practices that build remote engineering teams diversely.
However, proactive compliance offers a massive strategic advantage:
- Reputation: Firms known for ethical data use attract top-tier, privacy-conscious engineers.
- Reduced Risk: Compliance minimizes the threat of debilitating fines.
- Innovation: Adoption of compliant AI tools can boost productivity; AI is projected to boost GDP significantly by 2033.
Case in point, global firms like Google and Amazon have successfully adapted their Polish operations to these standards, leveraging the secure regulatory environment to build trust with European clients.
Avoiding costly mistakes when hiring, such as ignoring IP laws or data privacy, is now easier for companies that embrace these regulations as a framework for excellence rather than a burden.
Conclusion
The landscape of EU regulations IT Poland is redefining what it means to hire in Europe’s tech hub. From the strict data protections of GDPR Poland to the ethical mandates of the AI Act Poland, compliance is now the baseline for sustainable growth.
These frameworks not only protect candidates but also elevate the quality and maturity of the Polish IT sector, positioning it as a safe harbor for global innovation.
As Poland’s AI Policy 2030 continues to drive the market forward, the window to establish a compliant, high-performing team is open. For seamless, regulation-compliant tech hiring in Poland, partner with RemoDevs, we are experts in sourcing vetted software engineers with 100+ successful placements.
Contact us today to build your compliant IT team.
Visit us
Find a moment in your calendar and come to our office for a delicious coffee
Make an apointment

